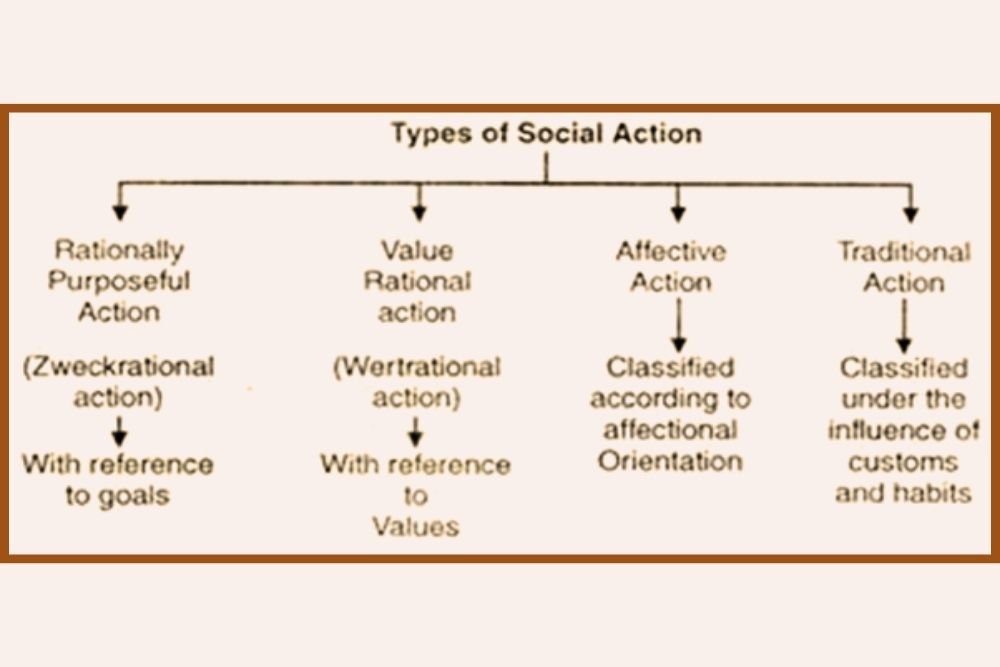
Neo-Marxism: Unraveling the Tapestry of Societal Dynamics
In the expansive realm of sociological thought, Neo-Marxism emerges as a vibrant and continually evolving perspective, offering a dynamic lens through which scholars engage with the intricate complexities of contemporary society. Building upon the foundational principles of classical Marxism, Neo-Marxism embarks on a transformative journey, synthesizing a diverse array of sociological insights to craft an intellectual tradition that provides nuanced analyses of power dynamics, class relations, and the multifaceted transformations unfolding within modern societies.
At its core, Neo-Marxism not only rekindles the Marxist emphasis on class struggle and economic structures but ventures beyond these boundaries, embracing a more comprehensive understanding of the intricate web of social complexities. One of the pivotal figures in the development of Neo-Marxist thought is Antonio Gramsci, whose exploration of cultural hegemony elevates the traditional Marxist framework. Gramsci's seminal work, "Prison Notebooks," introduces the concept that ruling classes not only maintain control through economic means but also wield influence through the shaping of cultural narratives and ideologies, highlighting the symbiotic relationship between culture and power.
The Neo-Marxist perspective gains further depth through the influential ideas of Louis Althusser, a thinker who accentuates the role of ideological state apparatuses in perpetuating capitalist ideologies. Althusser's comprehensive work, especially "Ideology and Ideological State Apparatuses," delves into how institutions like education and media become instrumental in reproducing capitalist norms and maintaining social hierarchies. This conceptualization expands the purview of Marxist analysis to encompass the subtle and pervasive ways in which ideologies are disseminated and internalized.
A notable departure within Neo-Marxism unfolds through the contributions of Ernesto Laclau and Chantal Mouffe in "Hegemony and Socialist Strategy." These scholars introduce the concept of post-Marxism, challenging traditional Marxist notions by acknowledging the multiplicity of social struggles that extend beyond class divisions. Laclau and Mouffe advocate for a more inclusive understanding of societal conflicts, recognizing the intersectionality of various forms of oppression and emphasizing the need for a flexible and adaptable analytical framework.
Another influential figure in the Neo-Marxist tradition is David Harvey, renowned for his book "The Condition of Postmodernity." Harvey's application of Marxist principles to the analysis of urban spaces and the global economy provides a unique perspective. His concept of spatial fix delves into how capitalism responds to crises by spatially reorganizing, often displacing economic problems rather than resolving them. This spatial lens offers a nuanced understanding of the geographical dynamics through which capitalism unfolds.
Examining Neo-Marxist perspectives on globalization leads us to the world-system theory proposed by Immanuel Wallerstein. In works like "The Modern World-System," Wallerstein interprets global capitalism as a complex system of economic and political relations. The framework of core, semi-periphery, and periphery nations, introduced by Wallerstein, offers valuable insights into understanding global inequalities and power dynamics, emphasizing the interconnectedness of nations within the broader context of capitalism.
The Neo-Marxist tradition also encompasses critical theorists such as Herbert Marcuse, whose work "One-Dimensional Man" provides a critical analysis of contemporary societies. Marcuse critiques the conformist nature of modern cultures, where individuals are assimilated into consumerist frameworks that serve the interests of the ruling class. His exploration of repressive tolerance reveals how seemingly tolerant societies might mask deeper forms of oppression, urging a reevaluation of societal structures and power relations.
In the expansive realm of sociology, Neo-Marxism continues to be a vital and evolving force, adapting to the ever-changing landscape of social realities. Its contributions extend beyond economic considerations, shedding light on the multifaceted nature of power relations in cultural, spatial, and global contexts. The ongoing dialogue within Neo-Marxist circles enriches the sociological discourse, providing valuable insights into the ever-evolving dynamics of power, class, and societal structures. As scholars within this tradition engage with diverse sociological perspectives, Neo-Marxism remains a dynamic and indispensable framework for understanding and challenging the complexities inherent in contemporary societies. The continual refinement of Neo-Marxist ideas attests to the intellectual vitality of this perspective, offering a robust theoretical foundation for scholars and students navigating the intricacies of societal dynamics.