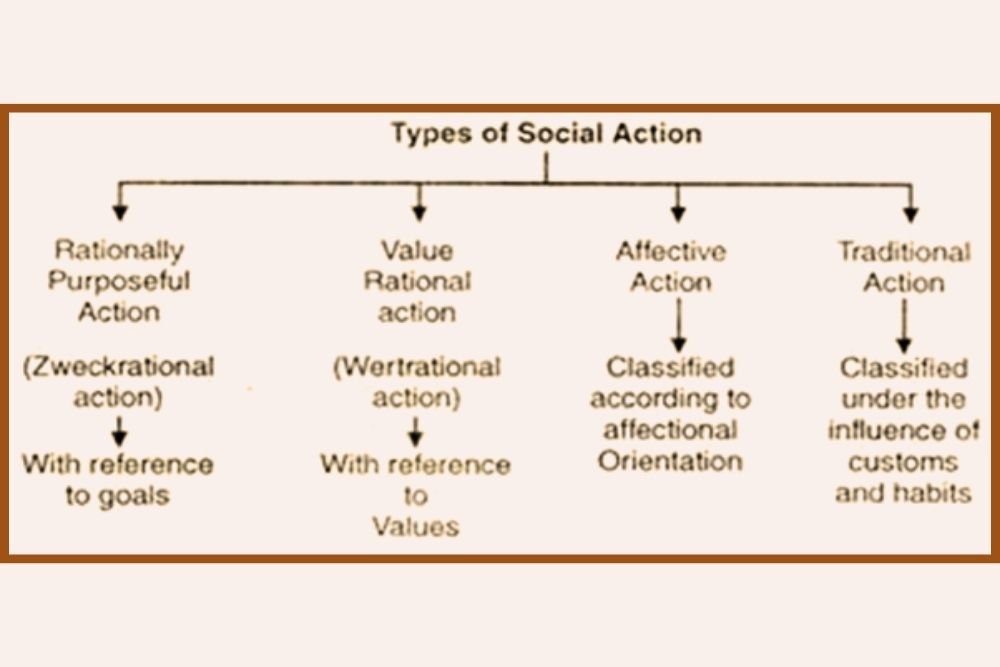
Indian Society: Structure and Change
- Perspectives on the Study of Indian Society
- (a) Indology (G.S. Ghure)
- Six features of caste
- Criticism
- (a) Indology (G.S. Ghure)
- (b) Structural functionalism (M. N. Srinivas)
- Sanskritization
- Dominant caste
- Criticism
- Caste,class and power
- (c) Marxist sociology (A. R. Desai)
- Impact of colonial rule on Indian society
- (a) Social background of Indian nationalism
- (The subaltern view, indological perspective etc)
- (b) Modernization of Indian tradition
- (c) Protests and movements during the colonial period.
- (d) Social reforms.
- (a) Social background of Indian nationalism
- Rural and Agrarian Social Structure
- (a) The idea of Indian village and village studies
- Jajmani system
- Analysis of Panchayati Raj institutions
- 73rd and 74th constitutional amendement
- Role of cooperatives in poverty alleviation
- (b) Agrarian social structure— evolution of land tenure system, land reforms
- Key features of land reforms
- Effectiveness of land reforms
- (a) The idea of Indian village and village studies
- Caste System
- (a) Perspectives on the study of caste systems
- Caste-Origin theories
- G. S. Ghurye
- M. N. Srinivas: Sanskritization,Ritual and secular hierarchy
- Louis Dumont:Purity and Pollution(Impure) theory
- Andre Beteille
- (b) Features of caste system
- Anuloma and Pratiloma
- Jajmani system
- Relationship between caste and varna
- Difference between caste and class
- Mobility in caste system
- Caste among non hindu communities
- Caste based census
- (c) Untouchability-forms and perspectives
- Ambedkar Vs Gandhi debate
- Constitution, law and social changes
- Dalit movements before independence
- Dalit movements post independence
- Contemporary trends in dalit movements
- Challenges faced by dalit movements
- Issue of Reservation
- (a) Perspectives on the study of caste systems
- Tribal Communities in India
- (a) Definitional problems
- Tribes and castes
- Classification of tribes
- (b) Geographical spread
- (c) Colonial policies and tribes
- (d) Issues of integration and autonomy
- Important tribal uprisings
- Three policy approaches for tribal development
- Tribal religious conversions
- Important tribal uprisings
- Constitutional provisions for tribal development
- Committees established for tribal development
- (a) Definitional problems
- Social Classes in India
- (a) Agrarian class structure
- (b) Industrial class structure
- (c) Middle classes in India
- Definitional problems of middle class
- Historical evolution of Indian middle class
- Political role of middle class
- New Middle class
- Systems of Kinship in India
- (a) Lineage and descent in India
- Definitions
- Different kinds of descent in India
- (b) Types of kinship systems
- Consanguinal kin and Affinal kin
- Kinship zones in India(Irawati karve)
- (c) Family and marriage in India
- Joint family system and its variations
- Changes in family structure in India
- Marriage within different religions
- Issue of surrogacy
- The issue of abortion
- (d) Household dimensions of the family
- Various types of households
- (e) Patriarchy, entitlements, and sexual division of labour
- Patriarchy in family structure
- Patriarchy and Religion
- Patriarchy and caste
- Patriarchy and politics
- Patriarchy and Media
- Women's movement in India
- Challenges before feminist movement in India
- Constitutional provisions for women empowerment
- Current issues revolving around rape, triple talaq, love jihad
- (a) Lineage and descent in India
- Religion and Society
- (a) Religious communities in India
- Various religious communities in India and interaction between them
- Socio religious movement during the colonial period
- (b) Problems of religious minorities
- Religious minorities in India
- (a) Religious communities in India
- Visions of Social Change in India
- (a) Idea of development planning and mixed economy
- LPG reforms and its impact
- Globalisation and its impact on India
- Critical assessment of globalization
- (b) Constitution, law, and social change
- Constitutional provisions triggering social change
- Contemporary issues like reservation on economic basis, Maratha reservation etc
- (c) Education and social change
- Functionalist and structural functionalist perspective
- Colonial policy on Education
- National Education Policy, 2020
- Evaluation of India's Education system
- Views on Education: Gandhi,Tagore,Nehru,Ambedkar,Sri Aurobindo,Dr S Radhakrishnan,other prominent scholars
- Effects of pandemic on Education
- (a) Idea of development planning and mixed economy
- Rural and Agrarian Transformation in India
- (a) Programmes of rural development, Community Development Programme, cooperatives, poverty alleviation schemes
- Village studies
- Views of Gandhi and Ambedkar on villages
- Academic view on villages
- Land reforms and its consequences
- (b) Green revolution and social change
- Impact on Indian society
- Political impact
- (c) Changing modes of production in Indian agriculture
- Feudal agrarian society and Capitalist industrial society
- Contemporary trends in Indian agriculture
- Challenges facing Indian farmers and solutions
- Agrarian class structure pre and post independence
- (d) Problems of rural labour, bondage, migration
- Phule on Agrarian labour
- Bonded labour
- Steps taken for elimination of bonded labour
- Problems of migration
- Pandemic induced migration
- (a) Programmes of rural development, Community Development Programme, cooperatives, poverty alleviation schemes
- Industrialization and Urbanisation in India
- (a) Evolution of modern industry in India
- Pre and post independence history of modern industries in India. (LPG Reforms etc)
- Views of Gandhi and Nehru on modern industries.
- (b) Growth of urban settlements in India
- Factors of urbanisation
- Theories of urban settlement(Concentric rings theory, Sector theory, Multiple Nuclei)
- Rural urban continuum
- Universalization and parochialization
- Impacts of urbanisation
- Urban issues like slums, sanitation etc
- Contemporary issues like Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Smart cities etc
- (c) Working class: structure, growth, class mobilization
- Evolution of working class in India
- Nature of working class in India
- Working class movements in India
- Impact of globalisation on working class
- (d) Informal sector, child labour
- Social implications of child labour
- Constitutional provisions
- Effects of pandemic on child labour
- Gender division of labour\ feminization of labour
- (e) Slums and deprivation in urban areas
- Issues surrounding prevalence of slums
- Possible solutions to the prevalent problems
- Challenges during and post pandemic
- Possibilities of slum reforms
- (a) Evolution of modern industry in India
- Politics and Society
- (a) Nation, democracy and citizenship
- Evolution of Indian political system
- Democracy in Indian and the western context
- Vote bank politics
- (b) Political parties, pressure groups, social and political elite
- Caste and Indian politics
- Caste based political movements
- (c) Regionalism and decentralization of power
- Causative factors fostering regionalism in India
- Positives and negatives of regionalism in India
- (d) Secularization
- Indian definition of secularism
- Causative factors for Indian secularism
- (a) Nation, democracy and citizenship
- Social Movements in Modern India
- (a) Peasants and farmers' movements
- Movements during colonial period
- Post independence movements
- New farmer movement
- Contemporary issues like Farm law agitation
- (b) Women’s movement
- (c) Backward classes & Dalit movements
- (d) Environmental movements
- (e) Ethnicity and Identity movements
- (a) Peasants and farmers' movements
- Population Dynamics
- (a) Population size, growth, composition and distribution
- World population trend
- (b) Components of population growth: birth, death, migration
- Determinants of population growth
- Causes and consequences of migration
- (c) Population Policy and family planning
- Phases in population growth in India
- Population policy in India and its assessment
- Family welfare programs
- (d) Emerging issues: ageing, sex ratios, child and infant mortality, reproductive health
- Social problems faced by the elderly
- MMR and IMR
- Issues surrounding contraceptives and usage
- Population control bill
- Lessons from China
- National policy for senior citizens
- Challenges of Social Transformation
- (a) Crisis of development: displacement, environmental problems and sustainability
- Sociological perspective on pandemic
- Summits on sustainable development
- Environmental movements in India
- Ideological strands of environmental movements
- Ecological feminism
- (b) Poverty, deprivation and inequalities
- Defining poverty
- Measures taken to reduce poverty
- (c) Violence against women
- Cyber Sexual harassment
- Contemporary issues like recent murders of women by partners(Shraddha Walker murder case etc)
- Patriarchial bargain
- (d) Caste conflicts
- (e) Ethnic conflicts, communalism, religious revivalism
- Colonial reasons behind the conflict
- Terrorism as a new form of asymmetrical warfare
- Current issues like Love Jihad, Riots Ethnicity and Race
- Racial hate
- Cultural revivalism
- (f) Illiteracy and disparities in education
- Measures to reduce disparities in education
- Contemperory issues like online education, the digital divide
- (a) Crisis of development: displacement, environmental problems and sustainability
- (a) Population size, growth, composition and distribution
Syllabus of Paper -1