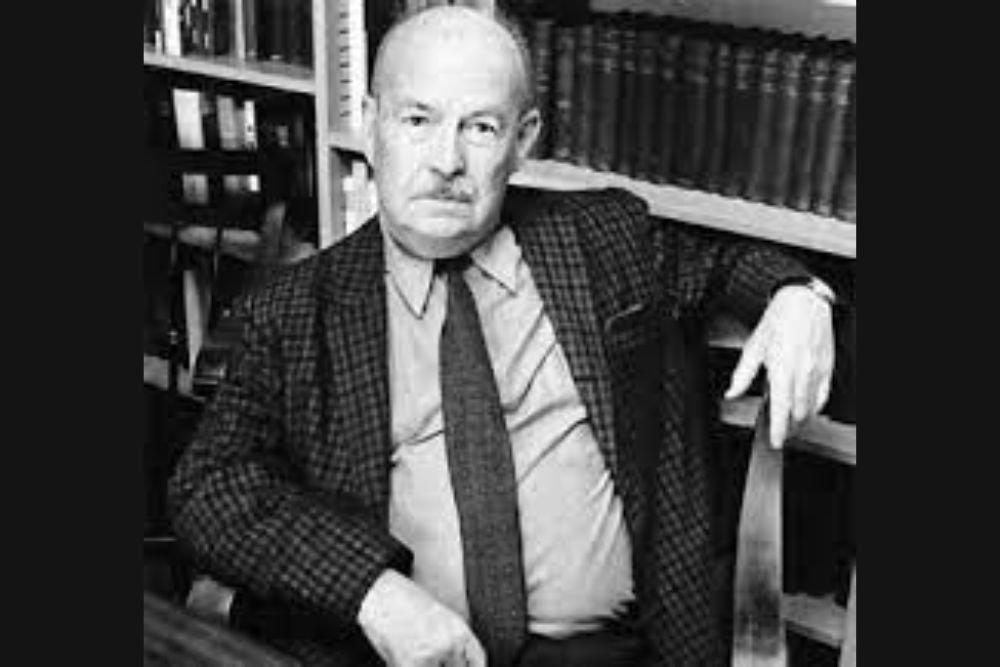
Talcott Parsons, a luminary in the expansive landscape of sociology, stands as an enduring figure whose intellectual contributions have profoundly shaped the discipline. Born in 1902, Parsons became not just a scholar but a beacon of thought, particularly through his influential work on structural functionalism. This theoretical framework seeks to unravel the intricate connections among diverse elements within a society, emphasizing their collective role in maintaining stability and ensuring the overall functioning of the social system.
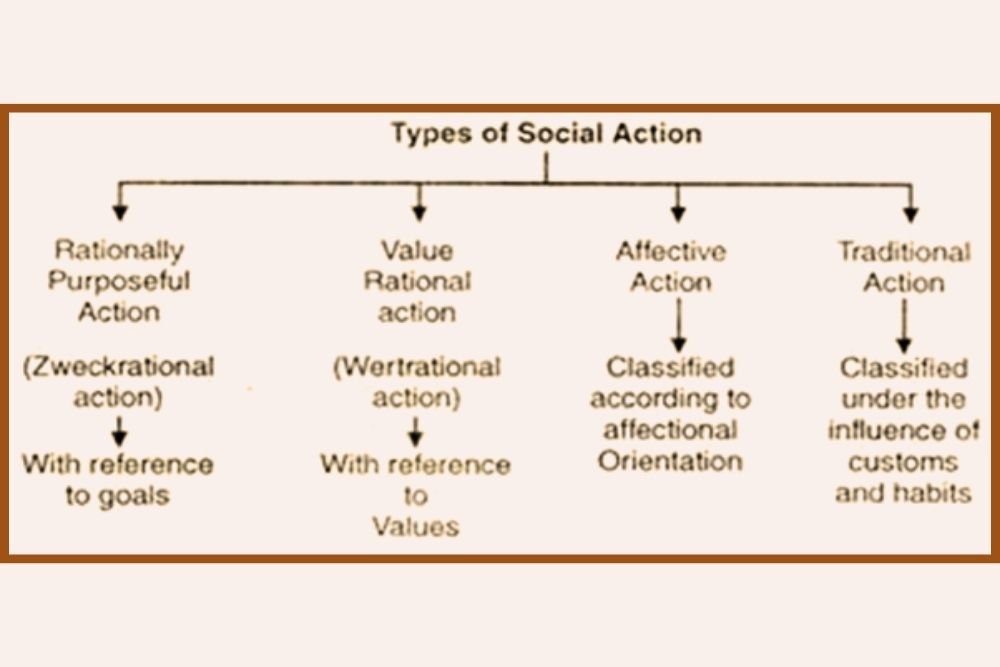
The linchpin of Parsons' intellectual odyssey is undoubtedly his groundbreaking opus, "The Structure of Social Action" (1937). This seminal work embarked on a profound and systematic dialogue with the ideas of Max Weber and Emile Durkheim, marking the initiation of a comprehensive exploration of social action. Serving as the fulcrum of his theoretical framework, this foundational piece not only set the stage for subsequent theories but also became a lodestar for sociologists grappling with the complexities of social relations across diverse temporal and cultural contexts.
The conceptual journey of Parsons' intellectual enterprise further unfolded with the introduction of the AGIL paradigm. This intricate model, encapsulating the functions of Adaptation, Goal Attainment, Integration, and Latency, aimed to provide a holistic understanding of the requisites for societal survival and evolution. The AGIL paradigm emerged as an indispensable analytical tool for sociologists, offering a nuanced lens through which to examine the intricate web of interdependencies within societies. It sparked reflections on the delicate equilibrium between stability and change, challenging scholars to navigate the complexities of dynamic social systems.
However, even amid accolades and influence, structural functionalism did not escape critical scrutiny. Some sociologists raised concerns about the framework's perceived conservative implications, arguing that its emphasis on stability might overshadow the intricate power dynamics and structural inequalities inherent in societies. This critique prompted a deeper reflection within the discipline about the necessity for theoretical frameworks capable of concurrently accounting for both stability and societal transformation.
Within the expansive tapestry of Parsons' intellectual contributions, the concept of pattern variables introduced in "The Social System" (1951) became a focal point of considerable debate. These variables, probing dimensions such as affectivity versus affective neutrality and specificity versus diffuseness, sought to categorize and comprehend social action. Nevertheless, scholars like C. Wright Mills contested this framework as overly abstract and detached from the nuanced complexities of real-world situations. This protracted debate underscored the persistent challenge of bridging the gap between theoretical constructs and the intricate realities of human interaction in society.
Beyond his theoretical oeuvre, Talcott Parsons' indelible influence extends to his role as a founding figure at the Harvard Department of Social Relations. Within this academic crucible, he played a pivotal role in mentoring and shaping the intellectual trajectories of a generation of sociologists. The legacy of his pedagogical influence resonates through the subsequent contributions of his students, who, inspired by Parsons, made significant advancements in the field.
In conclusion, Talcott Parsons' intellectual journey not only defined an epoch in sociology but also laid the groundwork for ongoing theoretical discourse. While critics may spotlight the limitations of his structural functionalist framework, there is no denying the profound and far-reaching impact he has had on the discipline. His exploration of social order, systems, and the intricate web of human interactions stands as a crucial reference point for sociologists navigating the multifaceted nature of society. This emphasis underscores the enduring relevance of his contributions in an ever-evolving sociological landscape, where scholars continually grapple with the complexities of the human social experience, seeking to deepen their understanding through the lens of Talcott Parsons' enduring intellectual legacy.