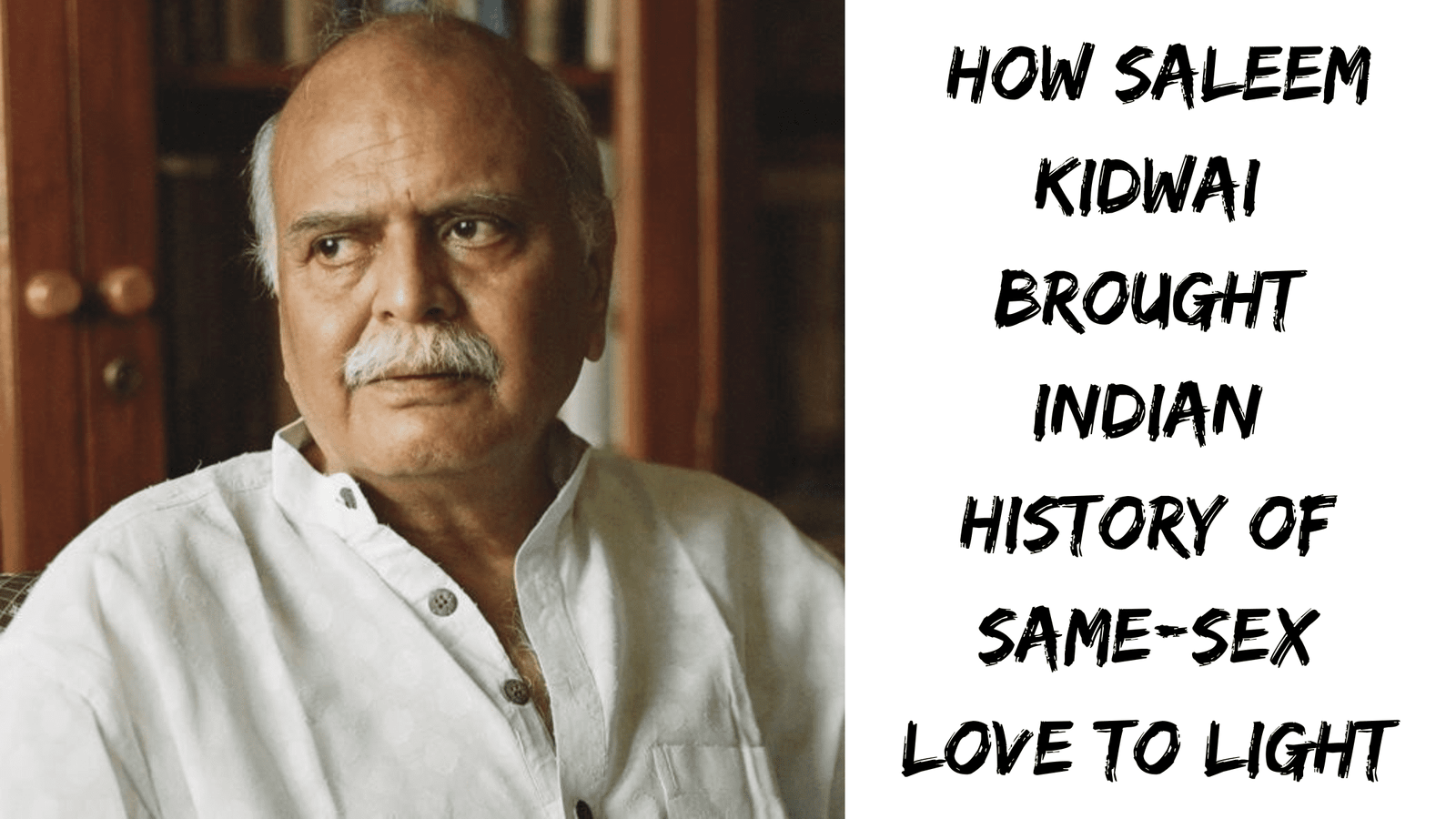The legalization of same-sex marriages is a topic that has gained considerable attention in recent years, both globally and within the context of India. Aspiring civil servants with a sociology optional need to grasp the sociological dimensions of this issue, utilizing relevant terminologies, theories, and concepts. This article aims to explore the sociological aspects of legalizing same-sex marriages in India, drawing upon the viewpoints of Indian and Western sociologists, significant sociological works, and relevant statistics to provide a comprehensive understanding of this social transformation.
Understanding Same-Sex Marriages:
Same-sex marriage refers to the legally recognized union between individuals of the same gender. It challenges the traditional understanding of marriage as a union solely between a man and a woman. By extending marriage rights to same-sex couples, societies aim to promote equality, inclusivity, and the recognition of LGBTQ+ rights.
Sociological Theories and Concepts
To comprehend the significance of legalizing same-sex marriages, it is crucial to delve into sociological theories and concepts related to gender, sexuality, and social change. The concept of heteronormativity, which privileges heterosexual relationships and marginalizes other forms of sexuality, plays a significant role in shaping societal attitudes toward same-sex marriages. The social construction of sexuality theory, as posited by sociologists such as John Gagnon and William Simon, highlights how social institutions and norms influence the formation and expression of sexual identities.
Viewpoints of Indian Sociologists:
Indian sociologists have contributed extensively to the understanding of LGBTQ+ rights and the significance of legalizing same-sex marriages in India. Scholars like Ruth Vanita, Ashwini Sukthankar, and Gautam Bhan have explored the sociocultural aspects of same-sex relationships in the Indian context. Vanita's work, "Same-Sex Love in India", critically examines the historical and cultural dimensions of same-sex relationships in India, challenging prevailing stereotypes and advocating for legal recognition. Sukthankar and Bhan's research explores the intersection of sexuality, gender, and urban spaces, shedding light on the complexities faced by LGBTQ+ individuals within Indian society.
Western Sociologists' Perspectives:
Western sociologists have also played a significant role in analyzing and theorizing same-sex marriages and LGBTQ+ rights. Scholars like Judith Butler and Michel Foucault have explored the social construction of gender and sexuality. Butler's concept of "gender performativity" challenges traditional binary notions of gender and emphasizes the fluidity and social construction of gender identity. Foucault's work, particularly "The History of Sexuality", examines the historical transformation of sexuality and the ways in which societies regulate and control sexual practices.
Implications and Societal Progress:
The legalization of same-sex marriages in India holds profound implications for society. It signifies a significant step towards achieving equality, dismantling heteronormative structures, and recognizing the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals. Legal recognition ensures access to benefits, social recognition, and the ability to form legally protected families. It also promotes greater acceptance and inclusion, contributing to a more tolerant and diverse society.
While precise statistical data on same-sex marriages in India is limited, global trends and studies offer insights into the social impact of legalization. Countries that have embraced same-sex marriages have witnessed positive outcomes, including improved mental health among LGBTQ+ individuals and increased social acceptance.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
The legal recognition of same-sex marriages in India represents a landmark moment in the pursuit of equality and LGBTQ+ rights. Approaching this issue through a sociological lens allows us to critically examine the implications, draw upon the perspectives of Indian and Western sociologists, and engage with relevant sociological theories and concepts. Aspiring civil servants equipped with this sociological understanding can actively contribute to shaping policies that promote equality and social justice for all individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Conclusion:
The legal recognition of same-sex marriages in India represents a landmark moment in the pursuit of equality and LGBTQ+ rights. Approaching this issue through a sociological lens allows us to critically examine the implications, draw upon the perspectives of Indian and Western sociologists, and engage with relevant sociological theories and concepts. Aspiring civil servants equipped with this sociological understanding can actively contribute to shaping policies that promote equality and social justice for all individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity.